
The Role of RBI’s Monetary Policy in Stock Price Movements
The Role of RBI’s Monetary Policy in Stock Price Movements
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), as the country’s central bank, plays a vital role in maintaining financial stability and driving economic growth. One of its most powerful tools is monetary policy, which influences interest rates, inflation, liquidity, and overall economic activity. For stock market investors, RBI’s policy decisions are closely watched since they can significantly impact stock prices, sectoral trends, and investor sentiment.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!What is RBI’s Monetary Policy?
RBI’s monetary policy refers to the framework through which the central bank manages money supply and credit availability in the economy. The primary objectives are:
-
Controlling inflation
-
Ensuring economic growth
-
Maintaining financial stability
-
Managing currency value
The RBI primarily uses instruments such as:
-
Repo Rate – The rate at which RBI lends to commercial banks.
-
Reverse Repo Rate – The rate at which RBI borrows from banks.
-
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) – Portion of deposits banks must keep with RBI.
-
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) – Minimum percentage of deposits banks must maintain in liquid assets.
-
Open Market Operations (OMOs) – Buying and selling of government securities.
How Monetary Policy Affects Stock Prices
1. Impact of Interest Rates
-
When RBI raises repo rates, borrowing costs for companies increase. Higher loan repayments reduce corporate profitability, leading to lower stock valuations.
-
Conversely, rate cuts reduce interest costs, boosting profits and stock prices.
Example: The rate hikes in 2022 to combat inflation led to corrections in rate-sensitive sectors like banking, real estate, and automobiles.
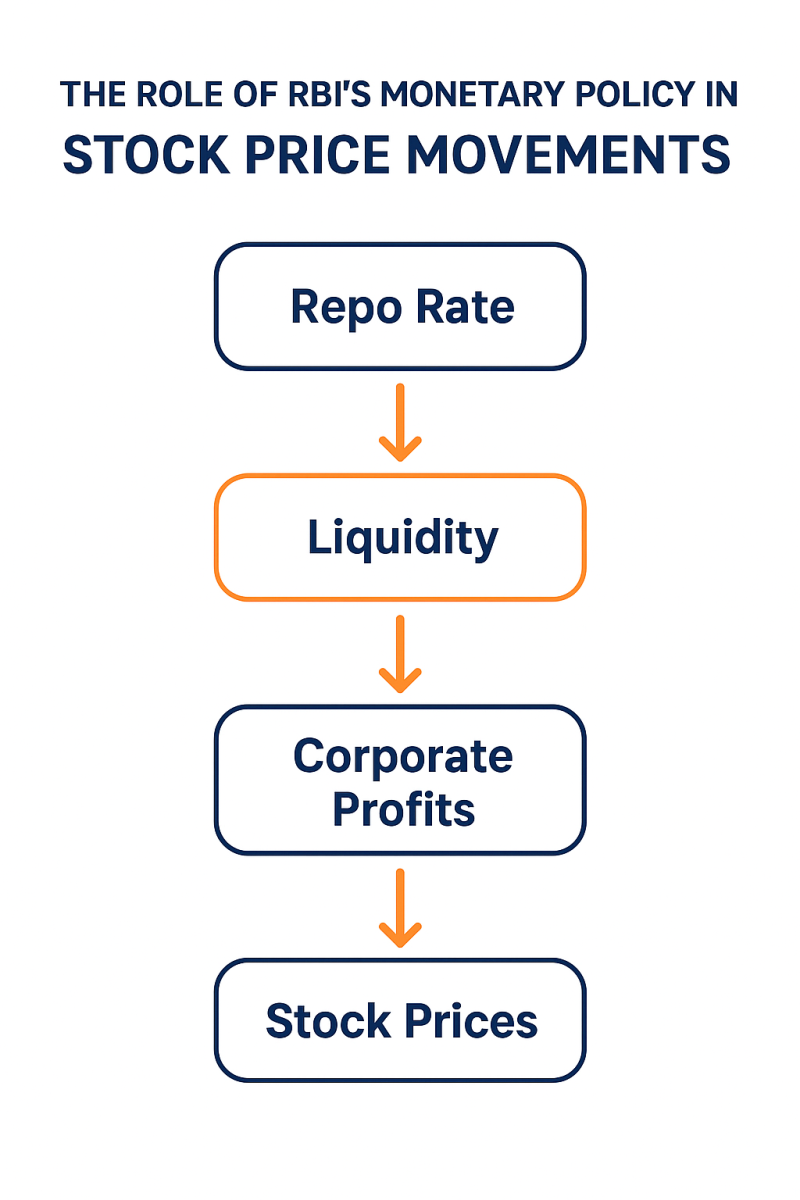
2. Liquidity in the System
-
Expansionary policy (lower rates, reduced CRR/SLR) injects liquidity, making more funds available for investments, driving stock market rallies.
-
Tight monetary policy (higher rates, increased CRR/SLR) withdraws liquidity, often resulting in market corrections.
3. Inflation Control
-
High inflation erodes purchasing power and corporate margins. RBI may raise rates to control inflation, which can negatively affect stock prices.
-
Stable inflation, backed by supportive monetary policy, creates a conducive environment for businesses and boosts investor confidence.
4. Currency and Foreign Investment
-
RBI’s policies affect the rupee’s strength. A weaker rupee may discourage foreign institutional investors (FIIs) from investing, leading to market outflows.
-
A stable currency, driven by balanced policies, attracts FIIs, supporting stock market growth.
5. Sectoral Impacts
Different sectors react differently to RBI policy moves:
| Sector | Effect of Rate Hike | Effect of Rate Cut |
|---|---|---|
| Banking & NBFCs | Higher borrowing costs, margin pressure | Loan growth improves, profitability rises |
| Real Estate | Demand slows due to higher EMIs | Demand picks up as home loans become cheaper |
| Automobiles | Vehicle loans costlier, sales decline | Sales improve with lower EMIs |
| IT & Pharma | Relatively less impacted | Benefit from stable currency & global demand |
| Infrastructure | Projects become costlier to finance | Boost from cheaper capital |
Case Studies
-
COVID-19 Pandemic (2020): RBI slashed repo rates to record lows and infused liquidity through OMOs. This accommodative stance triggered a massive rally in Indian equities.
-
2022 Inflationary Pressures: RBI increased repo rates multiple times to curb inflation, leading to short-term corrections in equity markets, especially in rate-sensitive sectors.
Investor Takeaways
-
Track RBI Announcements: Every bi-monthly monetary policy review has the potential to shift market momentum.
-
Focus on Sectoral Impact: Identify which industries benefit or suffer most from rate changes.
-
Balance Short vs Long Term: While short-term volatility is common, long-term market direction depends on the overall economic health fostered by RBI policy.
-
Diversify: A mix of defensive and cyclical stocks can balance risks arising from monetary shifts.
Final Thoughts
RBI’s monetary policy is a cornerstone of India’s financial system, influencing stock prices through interest rates, liquidity, inflation, and foreign capital flows. While rate hikes may create short-term challenges, they ensure long-term stability by keeping inflation under control.
For investors, understanding and anticipating RBI’s policy actions can provide a significant edge in navigating stock market movements. Staying informed, diversified, and aligned with the central bank’s economic outlook is key to making smarter investment decisions.

