
Swing Trading Vs Positional Trading: Which Suits You Better in India?
Swing Trading Vs Positional Trading: Which Suits You Better in India?
When it comes to trading in the Indian stock market, one of the biggest questions new traders face is:
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!👉 Should I become a swing trader or a positional trader?
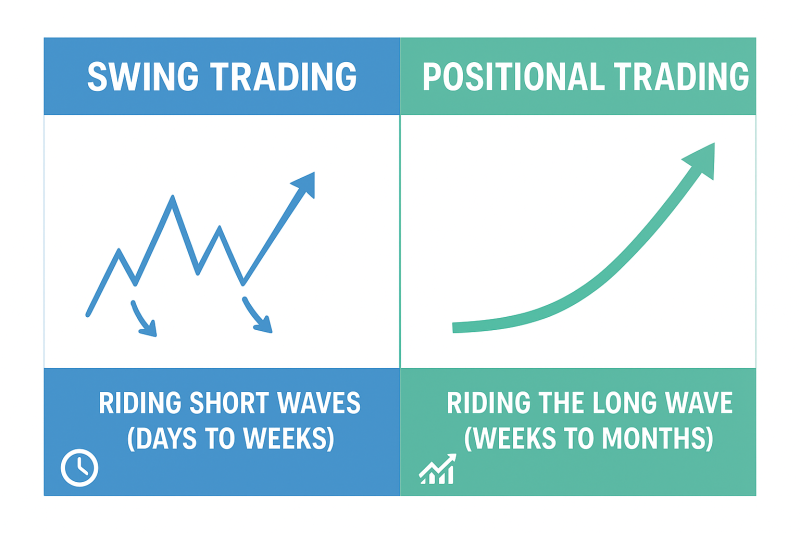
Both trading styles can be profitable, but they require different levels of patience, capital, and market analysis. Understanding the difference will help you decide which strategy fits your personality, goals, and risk appetite.
What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is all about capturing short-term price movements in a stock. Traders typically hold positions for a few days to a couple of weeks to take advantage of market swings caused by news, earnings, or technical setups.
Key Features of Swing Trading:
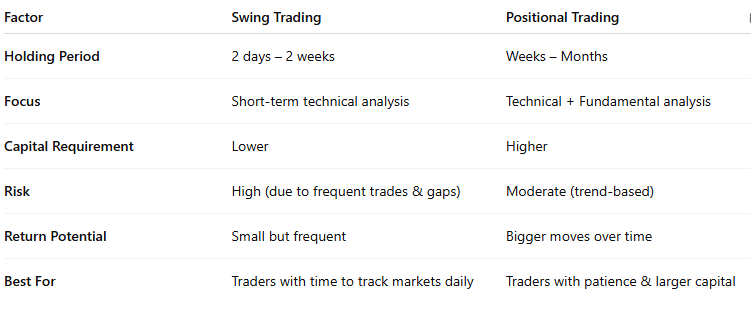
- Holding period: 2 days to 2 weeks.
- Focus on technical analysis of stocks (RSI, MACD, candlesticks, support & resistance).
- Higher trading frequency compared to positional investing.
- Quick profits but higher exposure to market noise.
Pros of Swing Trading:
✅ Quick capital turnover.
✅ Ideal for volatile markets like Nifty & Bank Nifty.
✅ Less stressful than intraday trading.
Cons of Swing Trading:
❌ Requires constant tracking of stock prices.
❌ Higher transaction costs (brokerage, taxes).
❌ Risk of overnight gap up/down moves.
Example in Indian Markets:
During results season, Infosys often sees strong short-term price swings. Traders use patterns like price-volume breakouts or Bollinger Bands to capture 5–10% moves within a week.
What is Positional Trading?
Positional trading is a medium-term strategy where traders hold stocks for weeks to months to benefit from broader market trends. This style combines both fundamental analysis of stocks and technical analysis.
Key Features of Positional Trading:
- Holding period: Several weeks to months.
- Focus on trend-following setups (moving averages, breakout confirmations).
- Relies on both stock fundamentals and sectoral outlook.
- Lower trading frequency than swing trading.
Pros of Positional Trading:
✅ Less affected by daily market noise.
✅ Can capture bigger price moves (20–50%).
✅ Lower brokerage and taxes compared to frequent swing trades.
Cons of Positional Trading:
❌ Requires larger capital & patience.
❌ Risk of sudden macro events (budget announcements, RBI policy).
❌ Not suitable for those wanting quick profits.
Example in Indian Markets:
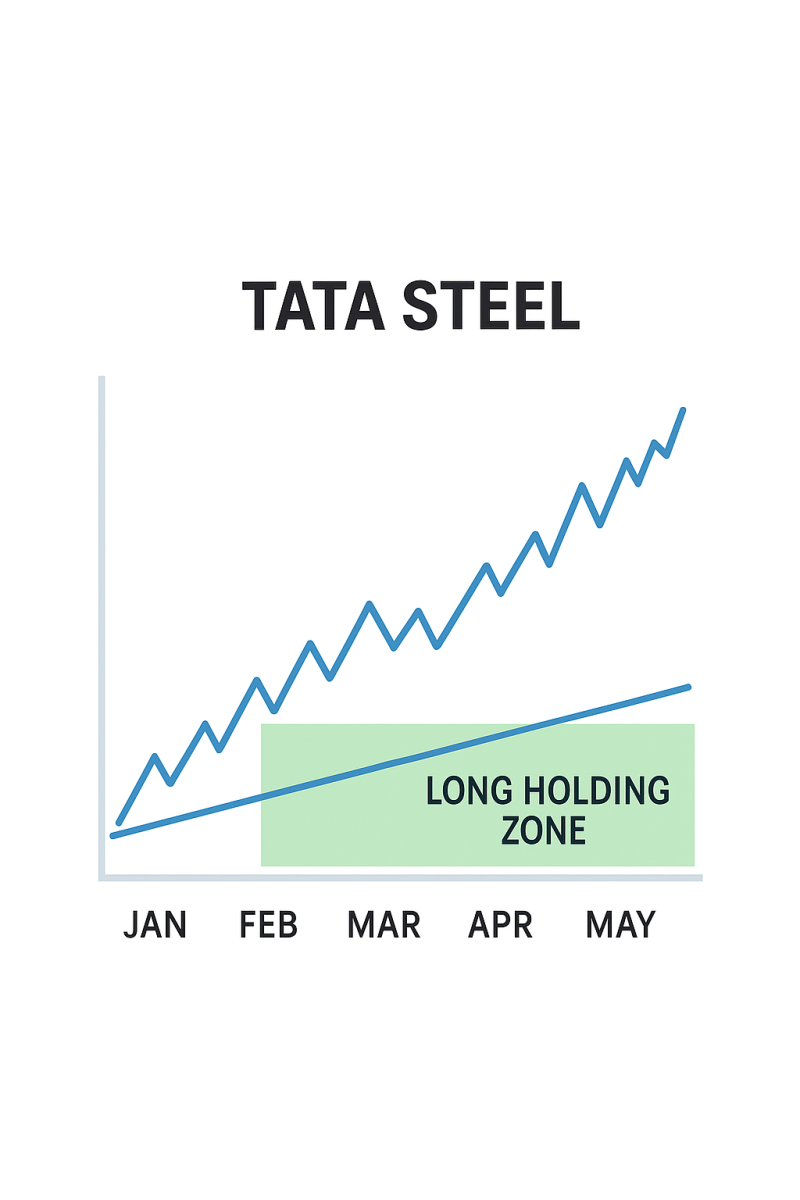
In 2020–2021, Tata Steel rallied for months as part of the commodities supercycle. Positional traders who identified the trend early booked massive gains, while swing traders had to settle for smaller chunks of the rally.
Swing vs Positional: Side-by-Side Comparison
Which One Should You Choose?
- If you are a beginner in stock analysis, want to learn how to analyse stocks in India, and don’t have time to watch markets every day → Positional trading suits you better.
- If you enjoy technical analysis of stocks, thrive in volatility, and want quicker returns → Swing trading may be your style.
- If your goal is wealth creation, you should also explore best stocks for long term investment in India, as neither swing nor positional trading replaces long-term investing.
Final Thoughts
Both swing trading and positional trading work in the Indian markets — the key is to match the strategy with your time availability, psychology, and risk appetite.
- Swing trading = More trades, faster profits, higher risk.
- Positional trading = Fewer trades, bigger gains, higher patience.
Smart traders often combine both — using swing trades for short-term gains while holding strong positional bets for long-term wealth building.
Related Blogs:
Stock Market Investment: Top 4 Equity Investment Tips for “Beginners”
What Is Fundamental Analysis? A Beginner’s Guide with Indian Context
How to Read a Company’s Balance Sheet: Step-by-Step with Indian Examples
Profit & Loss Statement: What Matters for Retail Investors in India
Cash Flow Statement: Why It’s More Important Than Net Profit
How to Analyze Management Quality Using Publicly Available Data
Key Financial Ratios Explained Simply (ROE, ROCE, D/E & More)
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. The financial data presented is subject to change over time, and the securities mentioned are examples only and do not constitute investment recommendations. Always conduct thorough research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.


