Understanding Futures & Options Trading in India
Understanding Futures & Options Trading in India
The Indian stock market offers multiple avenues for investors and traders to participate in wealth creation. While equities and mutual funds are popular choices, derivatives trading — specifically Futures & Options (F&O) — has gained significant traction in recent years. For those looking to diversify, hedge, or speculate, understanding how futures and options work is essential.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!What Are Derivatives?
Derivatives are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset such as stocks, indices, commodities, or currencies. In India, equity derivatives are among the most widely traded instruments on the NSE and BSE.
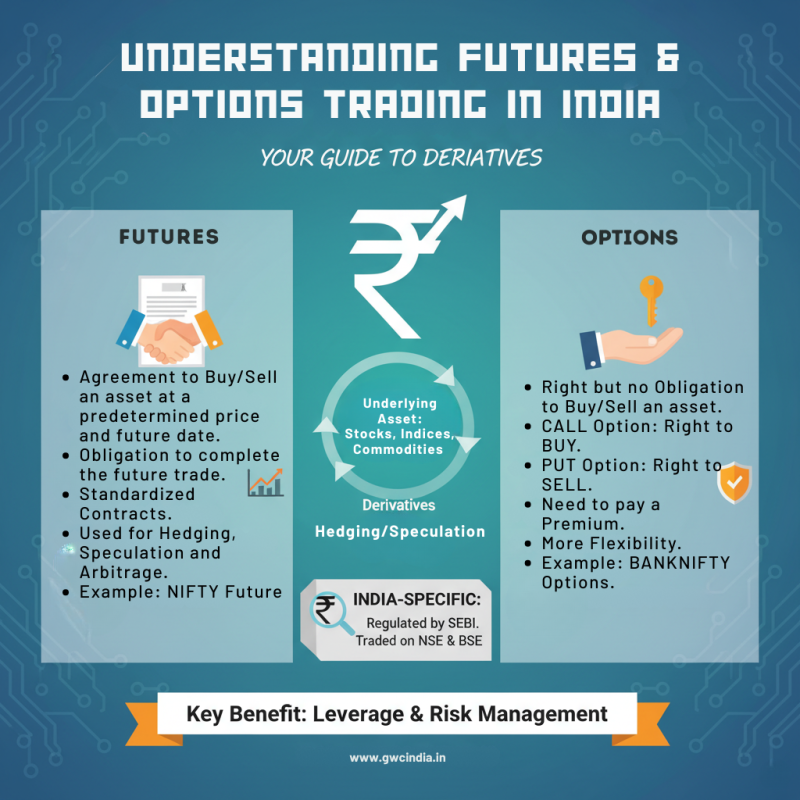
Futures Trading
A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date.
-
Example: If you buy Nifty 50 futures at 25,000, you are betting the index will rise above that level by expiry. If it does, you make a profit; if not, you face losses.
Key Features of Futures:
-
Standardized contracts traded on exchanges.
-
Require margin money (a small percentage of the total contract value).
-
Carry unlimited profit and loss potential.
-
Used for speculation and hedging.
Options Trading
An options contract gives the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy (Call Option) or sell (Put Option) an asset at a set price before expiry.
Types of Options:
-
Call Option (CE): Right to buy.
-
Put Option (PE): Right to sell.
Key Features of Options:
-
Buyer pays a premium to the seller (writer).
-
Limited risk for buyers (loss capped at the premium).
-
Sellers (writers) face higher risks but earn premium income.
-
Useful for hedging, speculation, and income generation.
Futures vs Options: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Futures | Options |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Contract | Obligation to buy/sell | Right but not obligation |
| Risk | Unlimited | Limited for buyer, unlimited for seller |
| Cost Involved | Margin money | Premium (paid by buyer, earned by seller) |
| Popular Use | Speculation, hedging | Hedging, speculation, income strategies |
Why Do Traders Use F&O in India?
-
Hedging: Protect portfolios from adverse price movements.
-
Speculation: Leverage to maximize returns on market moves.
-
Arbitrage: Profit from price differences in cash and futures markets.
-
Income Generation: Through option writing strategies.
Risks Involved in F&O Trading
-
Leverage Risk: Small margin can amplify both profits and losses.
-
Complexity: Requires deep understanding of pricing, volatility, and strategies.
-
Liquidity Risk: Some contracts may not have enough buyers/sellers.
-
Psychological Pressure: High volatility can lead to emotional decision-making.
Regulatory Framework
-
In India, F&O trading is regulated by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
-
Contracts are listed and traded on NSE and BSE.
-
Retail participation has surged in recent years, but SEBI emphasizes caution due to high risks.
Final Thoughts
Futures and Options trading can be powerful tools for investors — whether to hedge risk, speculate on market moves, or generate income. However, they are not suitable for beginners without adequate knowledge, as risks can be substantial.
If you are new to F&O, start by understanding the basics, practice with small positions, and gradually build expertise. For most retail investors, F&O should complement, not replace, long-term investments in equities and mutual funds.