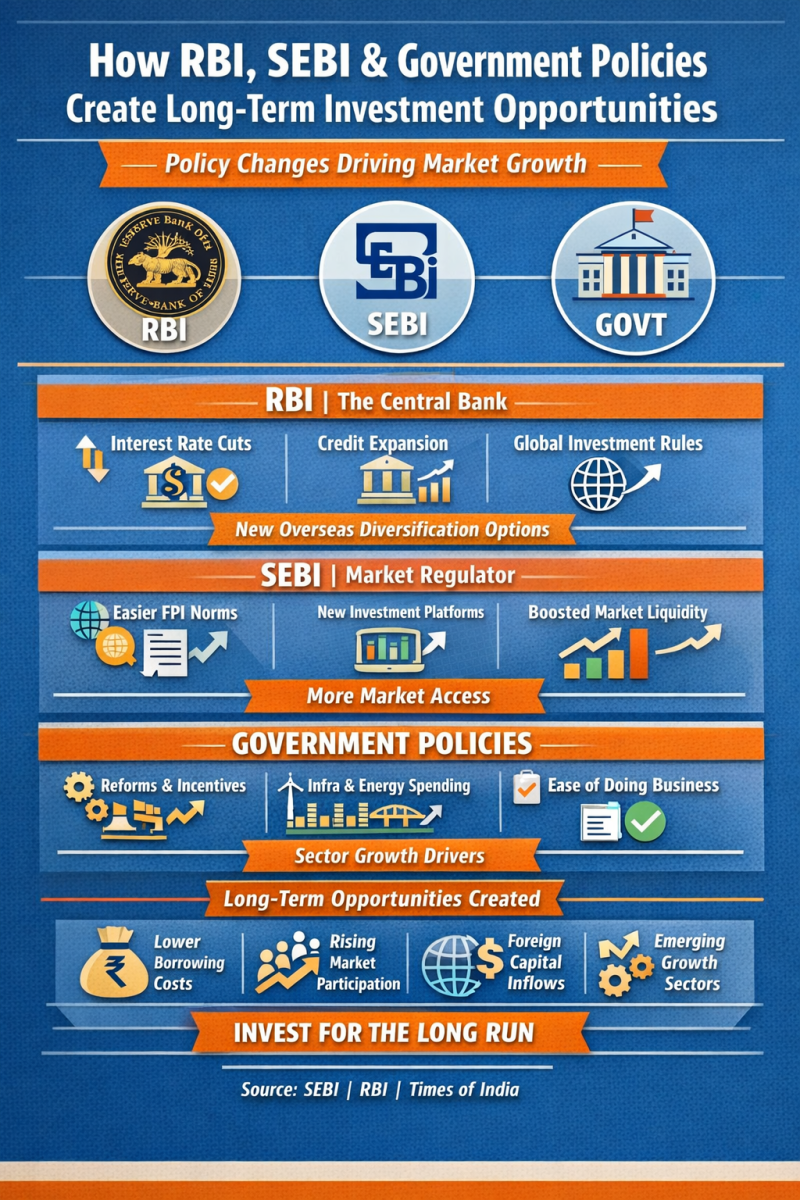
How Do RBI, SEBI, and Government Policy Changes Create Long-Term Investment Opportunities?
How Do RBI, SEBI, and Government Policy Changes Create Long-Term Investment Opportunities?
In India’s investment landscape, macroeconomic policy, central banking actions, and regulatory reforms play a major role in shaping the stock market and broader financial ecosystem. For retail and emerging investors, understanding how changes from institutions like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and government policies influence markets can uncover durable investment opportunities—not just short-term trading signals, but structural shifts that support sustained growth.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!This article explains how policy changes impact capital flows, cost of capital, credit availability, market access, risk premium, and ultimately, long-term investment returns.
1. Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Monetary Policy and Credit Dynamics
The RBI is India’s central bank, and its policy actions directly affect financial conditions, liquidity, and economic growth.
Monetary Policy and Liquidity
RBI uses tools like the repo rate (rate at which it lends to banks) and reverse repo (rate it borrows from banks) to manage the cost and availability of credit. These instruments, collectively part of monetary policy, influence borrowing costs across the economy. Lower interest rates reduce corporate financing costs, often boosting capital expenditure, profitability, and stock valuations.
When the central bank injects liquidity, equities and credit markets often rally as borrowing becomes cheaper and risk appetite improves.
Credit Flow and Financial Support for Growth
Changes in bank lending norms can also create investment opportunities. For example, the RBI has proposed adjustments to bank exposure limits in capital markets and acquisition financing, allowing banks to lend more for mergers and acquisitions and capital market activities.
Why this matters for investors:
-
Corporate expansion and consolidation can accelerate growth in sectors poised for scale.
-
Acquisitions often unlock synergies and structural growth.
-
Easier acquisition financing can benefit both acquiring and target companies.
Such reforms can indirectly support valuations of companies in sectors favored by consolidation or expansion capital.
RBI’s Overseas Investment Regulations
RBI’s overseas investment rules directly affect Indian capital flows abroad. Recent changes have expanded the types of vehicles Indian investors can use for international diversification, making it easier to invest in global markets through IFSC (International Financial Services Centre) structures.
Opportunity angle:
-
Indian investors can diversify risk and capture global trends—often earning higher returns than domestic-only portfolios.
2. SEBI: Deepening Capital Markets and Enhancing Participation
SEBI regulates India’s securities markets. Its reforms affect how investors access markets, trade instruments, and participate in capital formation.
Boosting Foreign and Institutional Investment
SEBI has eased compliance norms for Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs), especially those investing in government bonds, simplifying onboarding and disclosure requirements.
Additionally, SEBI is proposing simplified compliance for FPIs in government bonds, aimed at attracting long-term capital inflows into Indian debt markets.
Implications for investors:
-
Increased foreign investment can reduce borrowing costs and strengthen credit market depth.
-
Higher demand for government securities may reduce yields, making equities and corporate bonds more attractive.
Expanding Market Access and Products
SEBI is also introducing frameworks such as SWAGAT-FI to streamline entry for trusted foreign investors and reduce compliance friction.
This single-window access model is expected to:
-
Lower regulatory hassles
-
Encourage global capital inflows
-
Improve liquidity across asset classes
Foreign participation often correlates with higher price discovery, deeper markets, and lower volatility—a positive for long-term investors.
New Investment Vehicles and Market Innovation
SEBI’s reforms frequently expand the range of financial products available to investors. For example:
-
Co-investment frameworks within alternative investment funds (AIFs) make early-stage investing more accessible in structured ways.
-
Broader access for foreign and domestic institutional investors in IPOs improves market stability and growth funding.
Investor takeaway:
Expanding product ecosystems help investors diversify across asset classes, risk profiles, and market segments—ideal for building resilient, long-term portfolios.
3. Government Policy: Structural Reforms and Sectoral Growth
Government fiscal and regulatory policies can create multi-year expansion opportunities by shaping entire industries.
Regulatory Reform and Ease of Business
Policies that enhance ease of doing business, reduce compliance costs, and encourage private investment often boost equity valuations. For example, reforms targeting infrastructure building, tax rationalisation, and digital economy initiatives expand corporate profitability and investment potential.
Government initiatives like Make in India, PLI schemes, and sector-specific incentives (e.g., semiconductor or renewable energy production linked incentives) improve competitiveness and attract long-term capital.
Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth
Government budgets and spending priorities affect demand for capital goods, infrastructure, and consumer industries. Fiscal support for key sectors increases public-private partnerships, demand for goods and services, and GDP growth—factors that often pre-empt corporate earnings expansion.
Regulatory Coordination Between RBI, SEBI, and Government
Coordination between regulators and policy arms accelerates execution of reforms. For example:
-
RBI aligning credit flow to GDP expansion
-
SEBI simplifying markets for global and domestic investors
-
Government aligning policy to growth drivers
This holistic approach can transform structural growth opportunities in sectors like banking, technology, renewable energy, and infrastructure.
How Policy Changes Translate Into Investment Opportunities
Understanding the mechanics of policy changes helps investors anticipate where growth is likely to occur.
1. Lower Cost of Capital
Monetary policy easing by the RBI lowers borrowing costs for companies, enabling:
-
Expansion projects
-
M&A activity
-
Share buybacks
-
Dividend growth
Companies with good credit profiles often benefit first.
2. Higher Market Liquidity and Participation
SEBI’s reforms attract both retail and institutional participants. Greater participation increases liquidity, reduces transaction costs, and typically supports higher valuations over the long term.
3. New Asset Class Development
Regulatory and policy changes often spur new asset classes—such as online bond platforms, REITs being reclassified to unlock mutual fund capital (global trend) or AIF innovations—offering investors diversified return streams.
4. Foreign Capital Inflows
Simpler compliance and relaxed entry rules for FPIs can push Sovereign Wealth Funds, pension funds, and long-term global capital into domestic markets. Foreign capital inflows historically correlate with favorable risk premia and performance in equities and bonds.
Examples of Long-Term Opportunity Zones
Banking & Financial Services
RBI’s policies on credit growth and capital market exposure directly influence lending capacity and financial intermediation.
Opportunity: Strong banks and NBFCs with prudent risk management may see expanded loan books and profit growth.
Capital Markets & Investment Platforms
SEBI’s OBPP and related frameworks have democratized bond investing for retail users, reflecting a broader policy push toward inclusive markets.
Opportunity: Retail investors can allocate to diversified fixed-income products with improved transparency and accessibility.
Foreign Investment-Driven Growth Sectors
Reforms easing FPI norms—especially into government securities and equity —may deepen markets and support infrastructure financing and corporate credit stability.
Opportunity: Long-term debt and equity strategies benefit from increased global capital participation.
Risks and Considerations
-
Policy changes may take time to be fully implemented and yield results.
-
Overreliance on foreign investor sentiment can increase volatility during stress.
-
Regulatory tightening may be needed to prevent asset bubbles.
Smart investors distinguish between short-term market reactions and long-term structural shifts.
Final Thoughts
Policy frameworks and regulatory changes are not abstract—they shape capital flows, risk pricing, investor confidence, and long-term economic growth. For retail and emerging investors, tracking developments from the RBI, SEBI, and government policy announcements is critical to identifying enduring investment opportunities rather than transient market noise.
By recognizing where reform is heading, investors can position portfolios for growth, diversification, and risk-adjusted returns across market cycles.
Sources with Links
-
SEBI eases compliance for FPIs in government bonds – simplifying investing for long-term global capital: SEBI | Ease of regulatory compliances for FPIs investing only in Government Securities
-
SEBI relaxes compliance to boost sovereign debt inflows – easing KYC and reporting for GS-FPIs: https://www.timesofindia.com/business/india-business/fpi-rules-sebi-eases-compliance-for-govt-securities-investors/articleshow/123813551.cms
-
Digital platforms & SEBI reforms democratize bond investing – improving accessibility for retail investors: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/markets/bonds/click-to-invest-how-technology-is-making-bonds-as-simple-as-buying-stocks/articleshow/123182162.cms
-
SEBI SWAGAT-FI & business reforms – unified access for trusted foreign investors: https://taxguru.in/sebi/sebi-board-approves-15-decisions-ease-business-reforms.html
-
RBI liquidity tools & monetary policy mechanics – repo and reverse repo operations: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liquidity_adjustment_facility
Related Blogs:
Impact of FIIs and DIIs on the Indian Stock Market
Understanding Market Sentiment: FII & DII Trends
Shareholding Pattern Analysis: What Promoters & FIIs Reveal About a Stock
Understanding Institutional Buying: How to Track Bulk & Block Deals in the Indian Stock Market
The Role of RBI’s Monetary Policy in Stock Price Movements
The Role of Working Capital Efficiency in Identifying Strong Businesses
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. The financial data presented is subject to change over time, and the securities mentioned are examples only and do not constitute investment recommendations. Always conduct thorough research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.